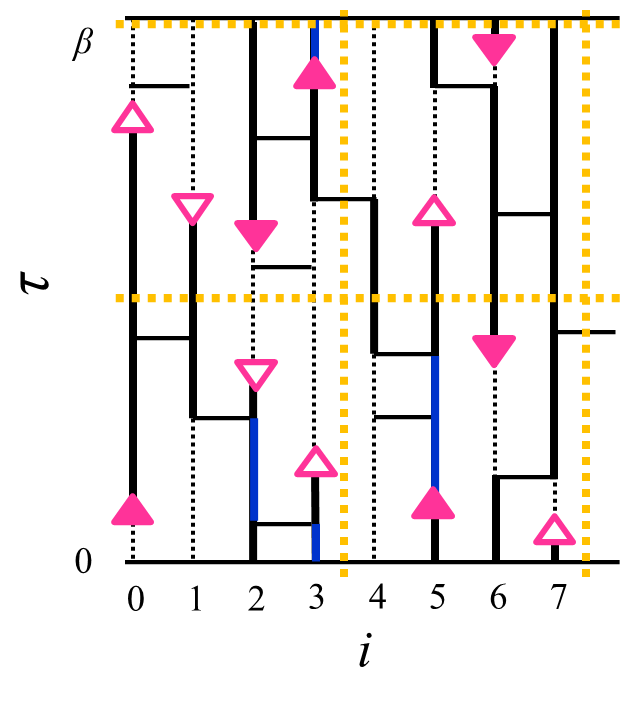
Based on the worm algorithm in the path-integral representation, we propose a general quantum Monte Carlo algorithm suitable for parallelizing on a distributed-memory computer by domain decomposition. Of particular importance is its application to large lattice systems of bosons and spins. A large number of worms are introduced and its population is controlled by a fictitious transverse field. For a benchmark, we study the size dependence of the Bose-condensation order parameter of the hard-core Bose-Hubbard model with L×L×βt=10240×10240×16, using 3200 computing cores, which shows good parallelization efficiency.
Reference
[1] N. Prokof’ev, B. Svistunov and I. Tupitsyn, Sov. Phys. JETP 87, 310 (1998) .[2] O. F. Syljuasen and A. W. Sandvik, Phys. Rev. E 66, 046701 (2012).
[3] A. Masaki-Kato, T. Suzuki, K. Harada, S. Todo and N. Kawashima, Phys. Rev. Lett. 112, 140603 (2014).